Treatment for Benign Lung Tumor: A Comprehensive Guide
Benign lung tumors, while often non-cancerous, can have significant implications for health and quality of life. Understanding the different treatment for benign lung tumor options is crucial for patients who are diagnosed with these growths. This guide provides a detailed overview of the nature of benign lung tumors, their diagnosis, and the latest treatment protocols available through specialized medical centers like Neumark Surgery.
Understanding Benign Lung Tumors
Benign lung tumors arise from the lungs' tissues but do not spread to other parts of the body. Unlike malignant tumors, benign tumors are generally not life-threatening; however, they can cause complications depending on their size and location. Common types of benign lung tumors include:
- Hamartomas: These are the most common benign lung tumors, consisting of an abnormal mixture of tissue.
- Myofibroma: A benign tumor largely composed of muscle tissue.
- Adrenal incidentalomas: While primarily associated with the adrenal glands, they can also present in lung tissue.
- Neurogenic tumors: Arising from nerve tissue in or near the lungs.
Signs and Symptoms of Benign Lung Tumors
Many individuals with benign lung tumors may remain symptom-free. However, symptoms can develop and may include:
- Persistent cough: A cough that does not resolve can indicate a need for medical evaluation.
- Shortness of breath: Large tumors may compress lung capacity.
- Chest pain: Localized pain can occur depending on the tumor’s location.
- Weight loss and fatigue: Unexplained weight loss or fatigue may require medical attention.
Diagnosis of Benign Lung Tumors
Effective diagnosis is critical for the appropriate treatment for benign lung tumor. Common diagnostic procedures include:
- Imaging tests: CT scans and MRIs provide detailed images of the lungs, allowing doctors to identify tumors.
- Biopsy: In some cases, tissue samples are taken for testing to confirm the benign nature of the tumor.
- Pulmonary function tests: Assess lung function to determine how well the lungs are working amidst the presence of a tumor.
Treatment Options for Benign Lung Tumors
The appropriate treatment for benign lung tumor largely depends on the tumor’s size, type, and associated symptoms. Here are the primary treatment options available:
1. Observation
Often, benign lung tumors are detected incidentally during imaging for other reasons. If the tumor is asymptomatic and not growing, your doctor may recommend a strategy of watchful waiting. This approach includes regular follow-up imaging to monitor changes over time.
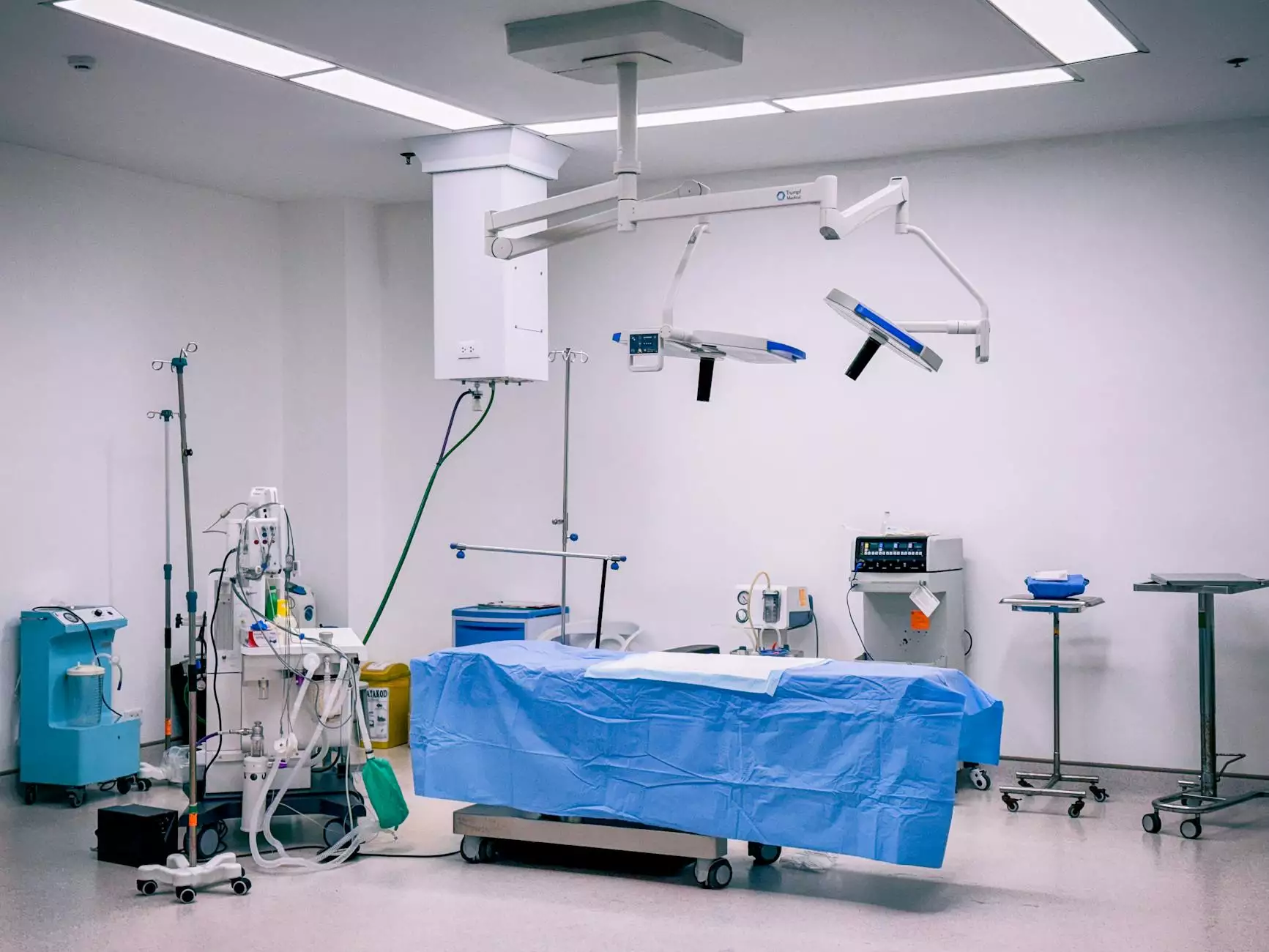
2. Surgical Removal
For tumors that cause symptoms or are growing, surgical intervention may be necessary. Types of surgery include:
- Wedge resection: Removal of a small section of lung tissue containing the tumor.
- Lobectomy: Removal of an entire lobe of the lung, which may be needed for larger tumors.
- Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS): A minimally invasive technique that allows for smaller incisions and faster recovery.
Surgeons at Neumark Surgery employ advanced techniques to minimize recovery time and surgical risk.
3. Medication
In certain cases, if the benign tumor is associated with specific symptoms or underlying conditions, managing symptoms with medications may be appropriate. These medications may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: To reduce inflammation surrounding the tumor.
- Pain relievers: To manage discomfort associated with the tumor.
4. Radiology and Non-Surgical Options
In selected cases, alternative non-surgical treatments such as radiation therapy might be considered, particularly if surgery poses significant risks. However, this is less common for benign tumors compared to malignant ones.
Post-Treatment Care and Follow-up
Post-treatment, it is crucial for patients to engage in regular follow-up appointments. Here are key aspects of post-treatment care:
- Routine imaging tests: Monitoring for recurrence or new growths is vital.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: A customized program may be necessary for patients recovering from surgery.
- Healthy lifestyle changes: Incorporating a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco can enhance recovery and overall lung health.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in Managing Benign Lung Tumors
The multidimensional care of patients with benign lung tumors often involves a team of healthcare providers, including:
- Pulmonologists: Specialists in respiratory health who play a key role in diagnosis and ongoing care.
- Thoracic surgeons: Surgeons specialized in lung surgeries who perform necessary procedures to remove tumors.
- Oncologists: Even benign cases may sometimes necessitate consultations with cancer specialists, particularly for suspicious growths.
Conclusion
The prognosis for individuals diagnosed with benign lung tumors is generally favorable, especially with advances in diagnostic imaging and surgical techniques. Early identification and appropriate intervention through specialized centers like Neumark Surgery can significantly impact outcomes. Patients experiencing symptoms or those concerned about lung health should seek prompt evaluation to determine the best course of action related to treatment for benign lung tumor.
By focusing on patient-centered care and leveraging advanced medical technologies, healthcare professionals can ensure that individuals with benign lung tumors receive comprehensive treatment that aligns with their health needs and goals.